During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes numerous changes, both physically and mentally. One significant transformation is the alteration in brain structure. You may have heard of “pregnancy brain,” where women experience difficulties in remembering or tend to forget planned tasks. However, this is not an illness but rather part of the natural changes occurring in the brain. So, what exactly happens to the brain during pregnancy? And how does this affect a mother’s memory and emotional bonding?
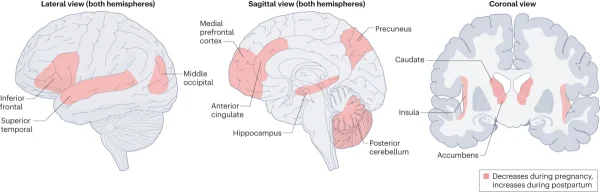
Recent studies have indicated that during pregnancy, the brain of a woman may reduce in size—a change that frequently occurs throughout pregnancy and only reverses after childbirth. An important study published in the journal Nature Neuroscience revealed a decrease in gray matter in the brains of pregnant women, especially in areas associated with social cognition and bonding. Nonetheless, this reduction is not detrimental; in fact, it enhances the mother’s ability to connect emotionally and understand her baby’s needs.
The research employed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques to monitor changes in the brains of pregnant women before and after delivery. The findings showed that the reduction in gray matter in specific regions does not impair the mother’s cognitive abilities; rather, it enables their brain to process nonverbal cues from the infant more effectively. This facilitates the recognition of potential risks and fosters a strong emotional bond with the child.
One explanation for this change is that during pregnancy, a mother’s body requires flexibility and adaptation to better prepare for postnatal care. Specifically, the decrease in gray matter in certain brain regions helps the mother more easily pick up on the silent signals from her newborn, allowing her to respond swiftly to the baby’s needs.
Importantly, this process also assists the mother in forming a closer bond with her child from the very first days after birth. The feelings of love and attachment become more intense, laying a solid foundation for the mother-child relationship. This is why, despite the structural changes in the brain, mothers are still well-equipped to meet the challenges of raising their children.
Another study published in the American Journal of Neuroradiology also demonstrated that the change in brain size among pregnant women is normal and does not have any adverse effects on their mental health or intellectual development. In reality, this change is temporary and tends to reverse approximately six months after childbirth, with the brain returning to its original size without compromising cognitive functions or communication skills.
Although these studies provide intriguing scientific insights, there are practical steps expectant mothers can take to support this process. Maintaining a healthy diet, ensuring adequate nutrient intake—especially the vitamins and minerals essential for brain development—can help enhance cognitive function and improve mental well-being throughout pregnancy.
Additionally, it is important for expectant mothers to get sufficient rest and minimize stress to reduce any negative impact on the brain. Engaging in gentle exercises, such as prenatal yoga, is also an effective way to keep the body flexible and maintain emotional balance.
With these scientific findings, we can be reassured that the changes in brain structure during pregnancy are a natural part of becoming a mother, aiding in the development of a deeper emotional connection between mother and child. Although some minor memory lapses may occur, this phase is only temporary and will resolve after delivery.
“A study published in Nature Neuroscience in 2019 demonstrated that the reduction of gray matter in key brain regions is not only a physiological response but also enhances the emotional connection between mother and child.”


HPX24h > Science > Can Pregnant Women Experience Temporary Memory Loss? The Secrets Behind Brain Changes During Pregnancy
Tagged Articles
Why Do Experts Believe Alzheimer’s Is an Autoimmune Disease Rather Than a Brain Disorder?
Direct Brain-to-Brain Communication via the Internet
Heart and Brain Health: How to Effectively Prevent Cognitive Decline?
Recreating the Mouse Brain in a Virtual World: The Future of Neuroscience
Top Reads from This Category
Science
Why Do Adult Brains Continue to Generate New Neurons?
Science
Successful Penis Transplant Surgery: A New Breakthrough in Medical Science
Science
New Artificial Kidney via Nanotechnology: A Revolutionary Alternative to Dialysis
Science
A New Era in HIV Prevention: Vaccine Set to Launch
Science
New Discovery: How the Brain Manages Emotions and Memory
Science
Gold in the Human Body: A Scientific Look at the ‘Hidden Gold’ Inside You
Science
AI Can Simulate Evolution and Create Proteins – A New Opportunity for Breakthrough Medical Therapies
Discover New Topics
Healthy Eating
How Much Protein Do You Need Daily: What’s Sufficient for Your Body
Parenting Tips
How to Talk to Children About Poverty and Homelessness (Ages 5-8)
Science
Stem Cell Therapy for Lung Cancer: A New Hope Entering Human Trials
Parenting Tips
Why You Can’t Force Your Child to Live the Way You Do?
Parenting Tips
How to Prevent a 2-Year-Old from Throwing Things?
Health
How Losing Just 5% of Your Weight Can Reduce the Risk of Diabetes
Animals
Ravens Use Gestures to Find Mates: A New Discovery About Their Intelligence
Science
New Hope from Cyborg Spinal Implant Technology for Paralyzed Patients
Health
Did You Know? Chronic Stress Can Prevent Your Body from Fully Recovering
Animals
The Care of Offspring: The Reproductive Secrets of Guppies
Fitness
The Secret to Holistic Health: Aerobics and Its Role in Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
Science
The First Person to Experience Physical Sensations Through a Prosthetic Hand
Fitness
HIIT: The Ultimate Shortcut to Efficient and Comprehensive Fitness