The decision to cut 168 jobs at the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), equivalent to 10% of its workforce, has sparked significant debate within the science and technology community. Some argue that this is a necessary strategy to optimize resources and reduce administrative costs, but many are concerned that this will be a mistake, weakening U.S. science in the long run. Is this decision truly a reasonable strategy, or is it simply a sign of weakening scientific standing for the country?
The beneficiaries of this decision may include large tech corporations such as Google, Tesla, and IBM, which have relied heavily on NSF’s basic research. With the reduction in public research funding, these companies will have the opportunity to expand their private investments in research, reducing dependence on government grants and gaining more control over the research they fund. However, the question arises whether these companies are willing to invest in basic research, or if they will focus only on short-term profitable research, such as consumer technologies or quickly commercialized products?
Companies like Google, Tesla, and IBM may take advantage of this reduction to control research more, but will they have enough motivation to fund basic research that does not immediately generate profits?
Furthermore, competing nations such as China, the EU, Japan, and South Korea may take advantage of this gap to attract talent from the U.S. China, in 2024, has increased its R&D budget by 15%, while expanding cooperation with countries such as the EU and Japan to develop strategic technologies like AI, quantum computing, and renewable energy. The EU is also increasing investments in these areas, while Japan is stepping up support for scientific research. This may cause the U.S. to lose its leading position in cutting-edge technologies, with other countries gradually surpassing it.
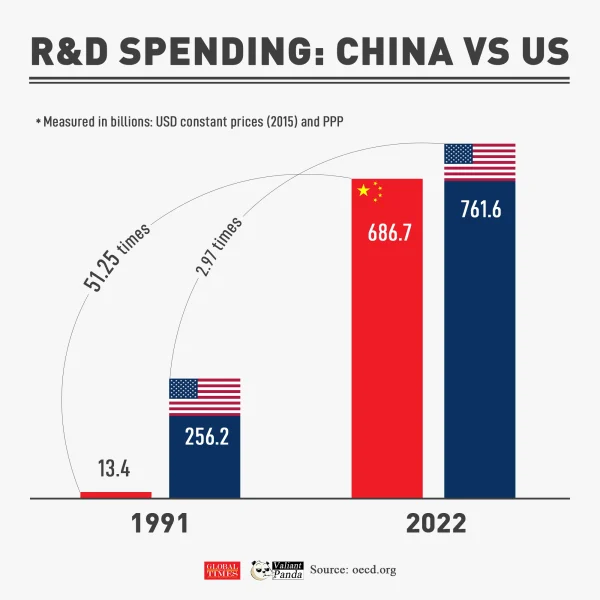
Caption: A chart comparing R&D budget growth rates between the U.S. and competing nations in 2024. China and the EU are ramping up research investments, posing a major challenge to the U.S.
Although the U.S. government may reduce budget pressure in the short term, this cut carries significant risks. Reducing the NSF’s budget may leave the government unable to fund basic research, thereby diminishing the innovation capacity of U.S. tech companies. At the same time, the government hopes the private sector will increase its investment in research, but this trend is not always guaranteed. Private companies may focus only on research with immediate profit potential, rather than investing in long-term foundational research, such as cutting-edge technologies that require long development times.
The private sector cannot completely replace government-funded basic research, as they can only focus on areas that provide immediate profits. Companies are not willing to invest in technologies that may take decades to develop, such as quantum computing or renewable energy research.
For those who will suffer the most, scientists and research institutes will be heavily affected. The 168 staff members at NSF who lost their jobs, including over 120 scientists at risk of losing funding, will lead to at least 35 critical research projects being paused or canceled. Key fields such as AI, renewable energy, and biotechnology will be stalled, slowing development in these industries. Moreover, talented scientists may leave the U.S. to seek research opportunities in countries with stronger research investment policies, such as China and the EU. This leads to the risk of a “brain drain,” where top researchers no longer see a future in the U.S.

U.S. tech companies will also struggle without sufficient basic research from NSF to support innovation. Without this research resource, companies will find it difficult to develop advanced technologies such as AI, quantum computing, and semiconductors. This will not only reduce America’s competitiveness but also eliminate its advantage in the technology race against rivals like China and the EU.
Lessons from the past also show the negative impact of cutting research budgets. In previous years, when the U.S. government reduced funding for basic research, large tech companies such as Microsoft and Intel had to ramp up private investment in research, but the lack of foundational research still created limitations in technology development. These budget cuts have had long-term consequences on the ability to develop cutting-edge technologies.
In conclusion, NSF’s decision may help reduce budget costs in the short term, but the long-term consequences could pose a significant challenge for the U.S. in maintaining its leadership in technology research and development. If the private sector cannot fill this gap, the U.S. will face the risk of falling behind in the global tech race. To ensure its competitive position, the U.S. needs a sustainable strategy for investing in basic research, along with close collaboration between the public and private sectors.
With these challenges ahead, the big question is: Which path will the U.S. choose to maintain its position in the global technology race? Will the U.S. government adjust its strategy and increase investment in scientific research, or will it allow other nations to surpass it?
Please read the next article: NSF Workforce Cuts – Which Path Will the U.S. Take to Stay Competitive in the Global Tech Race?


HPX24h > Science > NSF Job Cuts: Who Benefits and Who Bears the Consequences?
Tagged Articles
NSF Cuts 168 Jobs – Is the U.S. Scientific Community in Danger?
NSF Workforce Cuts – Which Path Will the U.S. Take to Stay Competitive in the Global Tech Race?
NSF Cuts 168 Jobs Amid Booming Science and Technology: Paradox or Strategic Move?
Top Reads from This Category
Science
Science Could Regrow Your Lost Arm… on a Monkey’s Body
Science
Successful Penis Transplant Surgery: A New Breakthrough in Medical Science
Science
Artificial Intelligence Outperforms Humans in Treating Depression
Science
Your Body Is Not the Same as It Was 10 Minutes Ago: The Continuous Regeneration Process of the Human Body
Science
Discover Blood Testing Technology Without a Visit to the Doctor
Science
A New Drug Could Treat Depression Within Just 24 Hours
Science
Implanting an NFC Chip into the Hand – When Technology and Humans Merge
Discover New Topics
Uncategorized
Why Do Experts Believe Alzheimer’s Is an Autoimmune Disease Rather Than a Brain Disorder?
Fitness
Active Recovery: The Key to Reducing Soreness and Boosting Workout Performance
Space
The Two Largest Black Holes Ever Discovered
Animals
Male Spiders Sacrifice Themselves to Protect Future Generations
Healthy Eating
Why Do We Need Fiber in Our Diet?
Parenting Tips
How to Prevent a 2-Year-Old from Throwing Things?
Science
A New Era in HIV Prevention: Vaccine Set to Launch
Healthy Eating
Does Drinking Water Help with Weight Loss? The Science Behind It and How to Apply It Properly
Space
Habitable Exoplanets: Exploring Distant Worlds
Health
The Best Days to Get Pregnant: How to Accurately Time Your Ovulation?
Fitness
Aerobic and Anaerobic: The Right Training Secrets for Overall Health and Strength
Science
Innate Intelligence: What Role Do Genetics Play in Developing High IQ
Fitness
Tai Chi: The Secret to Improving Balance and Relieving Pain Effectively