In recent years, stem cell technology and tissue engineering have made significant advancements in developing treatments for severe digestive disorders. One of the biggest breakthroughs is the ability to grow artificial gut tissue, offering new hope for patients with digestive disorders such as ulcerative colitis, bowel obstruction, or Crohn’s disease. Recent studies have shown that stem cells can be used to regenerate damaged gut tissue, providing a potential solution for treating these conditions.
A research team led by pediatric surgeon David Hackman at Stanford Medical School has successfully cultivated layers of intestinal mucosa on scaffold structures that mimic the shape of the intestine. Stem cells from the small intestines of newborns and mice were grown on these scaffolds, allowing the gut tissue to develop similarly to real intestines, with villus structures that help absorb nutrients. This technique not only overcomes previous difficulties in growing gut tissue on flat surfaces but also opens up a new avenue for treating digestive diseases.
“We have developed a new method that allows us to culture gut tissue on tubular scaffolds, enabling the tissue to grow properly, with villus structures for nutrient absorption. This is a major step forward in treating digestive disorders,” said David Hackman in a study published in 2024.
In one of the experiments, the research team transplanted gut tissue cultured from mouse stem cells into surrounding tissues in the mouse abdomen. This gut tissue developed its own vascular system, recreating the structures of the intestine, although it was not yet connected to the actual digestive system. However, the scientists saw this as an important step in creating gut tissue that could function like real intestines.
“We still have a long way to go in testing the nutrient absorption capabilities of this gut tissue in live animal experiments. But this is the first step in bringing this technology into therapeutic applications,” added David Hackman.
In another experiment, the team transplanted intestinal mucosa from dogs onto scaffolds. After some time, the tissue grew back and was able to perform the function of absorbing water from the large intestine. After a few weeks, the scaffolds dissolved and were replaced by normal connective tissue, allowing the dogs to fully recover.
This demonstrates that the ability to replace damaged gut tissue with cultured artificial tissue could be a feasible solution in the future. The cultured gut tissues could not only help treat severe conditions but also restore intestinal function for patients facing serious digestive problems such as necrotizing enterocolitis or Crohn’s disease.
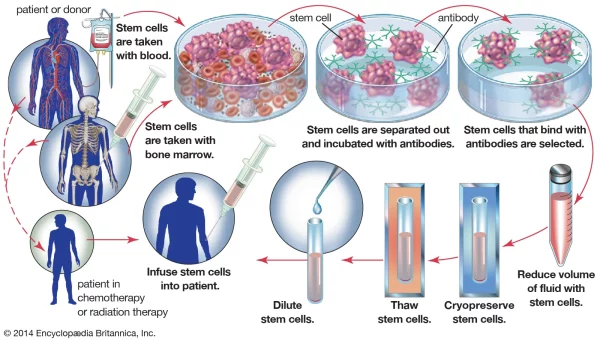
Although this technology promises significant benefits in medicine, many challenges remain. Researchers still need to test the nutrient absorption abilities of the artificial gut tissue in live animal experiments and find alternative materials to collagen, an essential component in helping stem cells adhere to the scaffolds. In future experiments, the research team plans to use surgical-grade collagen products, which could pave the way for the potential application of this technology in humans.
However, the initial successes of artificial gut tissue culture technology are giving hope to millions of patients worldwide, especially those with hard-to-treat digestive diseases. Stem cell technology could be the key to solving complex digestive issues, opening a new era in regenerative medicine, and offering a healthier life for those with gut disorders.


HPX24h > Science > Stem Cells and Gut Cultures: Unlocking New Possibilities for Treating Digestive Disorders
Top Reads from This Category
Science
Work 3.5 Days a Week and Live to 100: This Could Be Your Future
Science
Blood Test: A Breakthrough in Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease
Science
A New Era in HIV Prevention: Vaccine Set to Launch
Science
The Secret of the Bee Brain: New Technology Enables Drones to Fly Independently
Science
Laser Therapy Could Help Regrow Your Teeth – Did You Know?
Science
China’s Hypersonic Jumbo Jet Could Cut Beijing to New York Flight Time to Just 2 Hours
Science
AI Can Make Life Easier, But Is It Harming Your Ability to Think Critically?
Discover New Topics
Health
Forgetfulness Can Bring Unexpected Evolutionary Benefits
Science
Mind-Controlled Prosthetics: A Groundbreaking Advancement in Medicine
Science
New Discovery: How the Brain Manages Emotions and Memory
Science
Direct Brain-to-Brain Communication via the Internet
Science
Stem Cell Therapy for Lung Cancer: A New Hope Entering Human Trials
Healthy Eating
The Reasons You Should Eat These Fruits During Pregnancy to Reduce Fatigue and Anemia
Space
Over 100 Billion Planets in the Milky Way: Astonishing Discoveries About the Universe
Science
Stem Cell Liver Regeneration: A New Solution for Patients with Severe Liver Failure
Healthy Eating
Gallbladder Protection Through Diet: Expert Guide and Practical Tips
Space
3D Lunar Map: A New Gateway to Understanding the Universe
Healthy Eating
Why Is Nutrition Research So Complex?
Health
Chemicals in Cosmetics That Could Increase Breast Cancer Risk – Did You Know?
Fitness
Exercise – The ‘Miracle Cure’ to Awaken Overall Health