Aging is one of the natural processes that we cannot avoid. However, studying and understanding this phenomenon could provide opportunities to slow down aging or even prevent serious age-related diseases. A recent study has introduced a new method of measurement that not only considers a person’s chronological age but also incorporates biological factors to determine their “physiological age.”
Scientists from the University of Dunedin (New Zealand) conducted a decades-long study tracking over 1,000 participants born between 1972 and 1973. The primary objective was to analyze the differences between physiological and chronological age, or the age listed on birth certificates. Surprisingly, the results revealed that a person’s physiological age could differ significantly from their actual age.
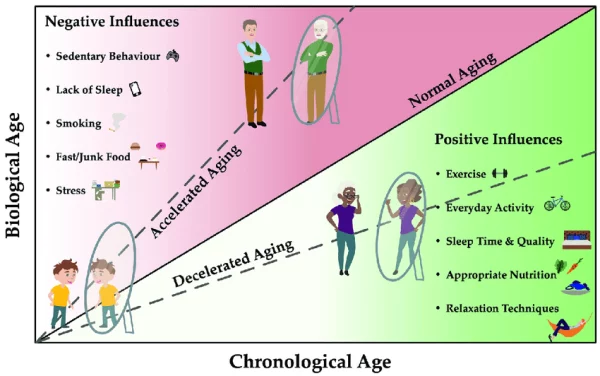
“Physiological age doesn’t always align with chronological age. We observed that participants aged 38 had physiological ages ranging from as young as 30 to nearly 60,” shared Dr. Dan Belsky, lead author and professor at the Center for Aging at Duke University (USA), in a paper published in Nature in 2020. This discrepancy was identified through the study of biological markers such as liver function, blood pressure, metabolic processes, and particularly telomere changes. Telomeres, the DNA segments that protect chromosomes, tend to shorten over time, serving as a clear indicator of cellular aging.
One of the standout findings from the study was that not everyone ages at the same rate. Among the participants, some maintained youthful health for many years with minimal signs of aging, while others aged rapidly—at a pace exceeding three years for every calendar year. This not only helps scientists better understand the aging process but also paves the way for interventions to slow aging, especially for younger individuals.
“The ability to measure physiological aging rates allows us to intervene early, slow the aging process, or target specific diseases,” explained Dr. Salomon Israel, co-author of the study and lecturer at Hebrew University (Israel), in a paper published in The Lancet in 2021.
This discovery opens up a promising future where not only is physiological age monitored and assessed, but timely intervention strategies can also be developed. The ultimate goal is not merely treating age-related diseases but addressing the aging process itself, enabling people to live healthier and longer lives. As this research becomes widely applied, it could lead to new health care and treatment methods, empowering individuals to take better control over their body’s aging process.
With these promising findings, physiological age measurement technology is expected to usher in a new era in aging research, helping humanity better understand their bodies and adopt more effective disease prevention strategies in the future.


HPX24h > Science > The Science of Measuring Biological Age: New Discoveries About the Aging Process
Top Reads from This Category
Science
AI Can Make Life Easier, But Is It Harming Your Ability to Think Critically?
Science
NSF Workforce Cuts – Which Path Will the U.S. Take to Stay Competitive in the Global Tech Race?
Science
Cow-Free Milk: The Food Revolution Shaping Our Future
Science
Discovery of a New Stem Cell: A Major Advancement in Creating Human Organs
Science
New Artificial Kidney via Nanotechnology: A Revolutionary Alternative to Dialysis
Science
Innate Intelligence: What Role Do Genetics Play in Developing High IQ
Science
Recreating the Mouse Brain in a Virtual World: The Future of Neuroscience
Discover New Topics
Health
Unlocking the Mystery: How the Brain Controls Body Weight
Healthy Eating
The Comprehensive Guide to the 16:8 Intermittent Fasting Diet
Healthy Eating
Does Drinking Water Help with Weight Loss? The Science Behind It and How to Apply It Properly
Space
Tidal Heating: A New Challenge for Extraterrestrial Life
Parenting Tips
How to Talk to Your Child About Smoking Issues
Fitness
More Flexible – The Secret to Longevity?
Fitness
Exercise Tips for Pregnancy: Safe, Effective, and Beneficial for Mom and Baby
Healthy Eating
Understanding the Important Role of Carbohydrates in Health
Parenting Tips
Fun Facts for 3-Year-Olds: Exploring the World of Animals and New Foods
Fitness
Cardiovascular Endurance: The Key to Optimizing Overall Health
Fitness
Mesomorph: The Key to Unlocking Your Body’s Natural Strengths
Animals
Unexpected Science: When Seismologists Listen to Underwater Earthquakes and Discover Whale Songs
Science
New Hope from Cyborg Spinal Implant Technology for Paralyzed Patients