A recent groundbreaking study has harnessed a dangerous natural substance—snake venom—to create a potentially life-saving drug, opening a new avenue in treating blood clot-related conditions. Scientists at Nanjing University, China, conducted an innovative study using genes that produce venom from the Agkistrodon acutus snake to transform yeast into a “factory” for producing proteins with anticoagulant properties. This marks a new advancement in biotechnology, merging nature and technology to develop safer pharmaceuticals.
Snake venom is one of nature’s most hazardous substances, but it contains components that have potential medical applications. Venoms from species like cobras and vipers have been studied for their effects in treating circulatory system diseases. However, natural venom is difficult to control and use, posing serious side effects such as excessive bleeding. As a result, utilizing snake venom in drug production has always been associated with significant risks.
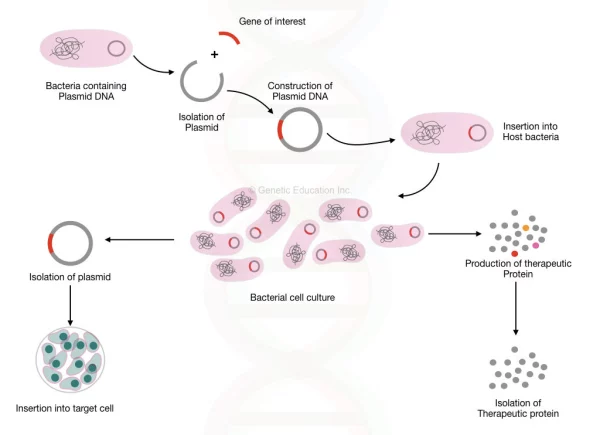
A research team led by Professor Xiao Weihua at Nanjing University has discovered a safer way to exploit this potential. Scientists extracted venom-producing genes from the Agkistrodon acutus snake and incorporated them into the genome of yeast cells. When cultured in a glycerol medium, these yeast cells were stimulated with methanol to produce venom proteins called Agkisacutalin, a natural anticoagulant. “The greatest value of Agkisacutalin lies in its minimal side effects, setting it apart from current anticoagulant drugs, which often cause severe bleeding,” Professor Xiao Weihua explained (*Source: Nanjing University, Nature Communications, 2023).
“This technology could revolutionize how we produce and use medications. By deriving products from natural sources like venom, we can create more effective and safer pharmaceuticals,” noted Professor Xiao Weihua (*Source: Nanjing University, Nature Communications, 2023).
This production system not only generates effective anticoagulant proteins but has also passed biosafety tests, showing significant potential for medical applications. However, scaling up production remains a major challenge. “Although we have succeeded in clinical trials, the technology faces obstacles, such as maintaining yeast viability after producing venom for 38 hours,” Xiao added (*Source: Nanjing University, Nature Communications, 2023).
One of the standout features of Agkisacutalin is its ability to replace traditional anticoagulants without causing dangerous side effects like excessive bleeding, a common issue with existing medications. These findings offer significant hope for patients requiring long-term anticoagulant therapy, especially those with cardiovascular diseases, strokes, or clotting disorders.
Agkisacutalin also holds potential for broader applications across various medical fields. Scientists believe this technology could extend beyond anticoagulants to treat autoimmune diseases, cancer, and even eye conditions like blindness. However, bringing this product to practical use will require overcoming challenges related to production scalability and costs.
“We are still in the process of refining and perfecting this technology. If successful, it could represent a major breakthrough in medicine, transforming how we treat clotting disorders,” said Professor Xiao Weihua (*Source: Nanjing University, Nature Communications, 2023).
Despite the technological and cost-related hurdles, this research has paved a new path for biotechnology. Utilizing wild animal genes to produce pharmaceuticals not only addresses challenges in drug production but also reduces reliance on synthetic chemicals. This technology promises a brighter future for healthcare, providing safer and more effective treatment solutions for critical health issues.


HPX24h > Science > Turning Snake Venom into Life-Saving Medicine: A Promising New Yeast Cell Technology
Top Reads from This Category
Science
The Mystery of the Brain Network that Regulates Human Attention Has Been Unveiled
Science
Discovering Enzymes That Stimulate Hair Regrowth: A New Opportunity in Hair Loss Treatment
Science
AI Can Simulate Evolution and Create Proteins – A New Opportunity for Breakthrough Medical Therapies
Science
Gold in the Human Body: A Scientific Look at the ‘Hidden Gold’ Inside You
Science
Why Cultured Meat Could Be the Future of the Food Industry
Science
New Discovery: How the Brain Manages Emotions and Memory
Science
Why Do Adult Brains Continue to Generate New Neurons?
Discover New Topics
Animals
Gibbons Develop Vocal Techniques as Powerful as Humans: New Discoveries About Their Unique Sounds
Healthy Eating
Moderate Coffee Consumption Helps Reduce the Risk of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases
Healthy Eating
Health is ‘Declining’ Due to Processed Foods: How to Turn the Tide
Fitness
Walking or Running: Which Is Better for Health and Weight Loss?
Science
Recreating the Mouse Brain in a Virtual World: The Future of Neuroscience
Parenting Tips
How to Talk to Your Child About Smoking Issues
Health
Unlocking the Mystery: How the Brain Controls Body Weight
Space
Scientists Discover Dark Galaxy Located 10 Billion Light-Years from Earth
Animals
Explaining How Mosquitoes Can Fly Through a Rainstorm
Science
Innate Intelligence: What Role Do Genetics Play in Developing High IQ
Animals
Can Hyena Dogs Be as Smart as Primates?
Science
Enhancing Memory with Brain Implants: A New Scientific Revolution
Fitness
HIIT Training: A Long-Term Remedy for Brain Health