When we think about the adult brain, most of us assume that its development has stopped. However, a groundbreaking discovery in neuroscience has changed this perception: the adult brain still has the ability to generate new neurons, particularly in areas related to learning, memory, and emotions. Why does the brain continue to produce new nerve cells even in adulthood? This finding not only opens up opportunities to better understand the brain’s adaptability but also holds significant potential for improving brain health and lifelong learning.
Neurogenesis (the process of creating new neurons) primarily occurs in the hippocampus, a region of the brain responsible for regulating memory and learning. Earlier studies suggested that this process only happened during developmental stages, but recent research has revealed that neurogenesis continues in the adult brain. A notable study by Lara Gould and colleagues, published in Nature Neuroscience in 2022, demonstrated that in stressful situations, the production of new neurons can be suppressed, leading to diminished learning and memory capacity. Conversely, positive experiences, such as rewards, can increase the number of new neurons, enhancing learning ability and reducing anxiety.
“Stress-induced suppression of adult neurogenesis has been associated with impaired performance in spatial navigation learning and object memory.” – (*Lara Gould et al., 2022, Nature Neuroscience).
This discovery reveals that the brain is not a static system but one capable of change and adaptation to its environment. It explains why humans can maintain learning and memory abilities throughout life. A sense of security and positive stimulation can promote neurogenesis, enabling adaptation to new situations. However, prolonged stress can reduce this ability, making it harder to learn and retain new information.
Although stress may inhibit the creation of new neurons, other studies suggest that neurogenesis can be stimulated through factors such as social environments and intellectual stimulation. Research by Elizabeth Gould and colleagues, published in Science in 2020, found that individuals engaging in rich physical or social activities were more likely to maintain and enhance neurogenesis compared to those living less dynamic or socially isolated lives.
“Increased social interactions and physical activities were shown to enhance neurogenesis in adult rodents, and similar results have been observed in humans.” – (*Elizabeth Gould et al., 2020, Science).
This adaptability of the brain benefits not only learning but also emotional regulation. The hippocampus, where new neurons are formed, plays a role in reducing anxiety and stress. Recent studies show that enhancing neurogenesis improves problem-solving skills and fosters a sense of security, thus mitigating anxiety and negative emotions.
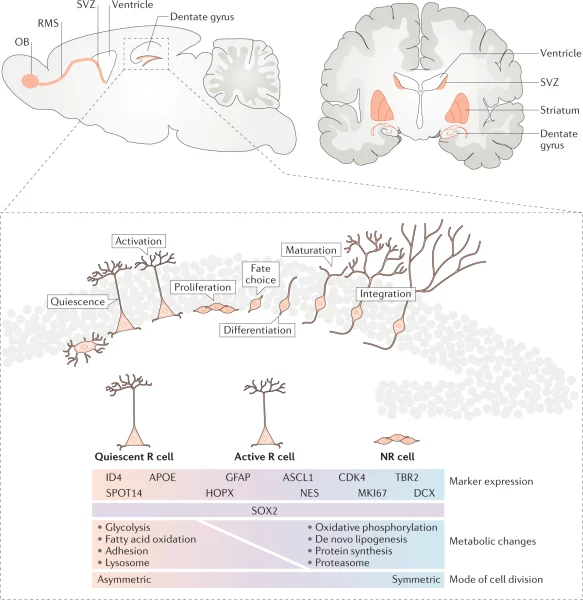
An important question arises: can we regulate neurogenesis to optimize learning and minimize memory issues? Current research suggests that a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and physical activity can positively impact the process of creating new neurons. A study by Terry L. J. Jones, published in Neuron in 2019, highlighted that sufficient sleep and an omega-3-rich diet could boost the development of new nerve cells in the adult brain.
“Adequate sleep and a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids were found to promote neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus.” – (*Terry L. J. Jones et al., 2019, Neuron).
This underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle to optimize neurogenesis. Living in a rich social environment and engaging in physical and intellectual activities not only benefits physical health but also enhances brain function. Habits like regular exercise and spending time on social relationships can stimulate the production of new neurons and keep the brain healthy.


HPX24h > Science > Why Do Adult Brains Continue to Generate New Neurons?
Tagged Articles
The Secret of the Bee Brain: New Technology Enables Drones to Fly Independently
Direct Brain-to-Brain Communication via the Internet
Heart and Brain Health: How to Effectively Prevent Cognitive Decline?
Recreating the Mouse Brain in a Virtual World: The Future of Neuroscience
Top Reads from This Category
Science
The Science Behind CRISPR: Can Animal Genetic Modification Lead Us to a Better Future?
Science
Discovery of a New Stem Cell: A Major Advancement in Creating Human Organs
Science
Successful Penis Transplant Surgery: A New Breakthrough in Medical Science
Science
Turning Snake Venom into Life-Saving Medicine: A Promising New Yeast Cell Technology
Science
Work 3.5 Days a Week and Live to 100: This Could Be Your Future
Science
The First Person to Experience Physical Sensations Through a Prosthetic Hand
Science
NSF Cuts 168 Jobs Amid Booming Science and Technology: Paradox or Strategic Move?
Discover New Topics
Parenting Tips
How to Talk to Children About Poverty and Homelessness (Ages 5-8)
Science
Blood Test: A Breakthrough in Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease
Health
The Mystery of Newborn Weight: How Does It Progress Each Month?
Science
Why Do Adult Brains Continue to Generate New Neurons?
Health
Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ Present in Bandages? How This Could Affect Your Health
Parenting Tips
Talking to Children About Race: How to Make It Easier?
Healthy Eating
How to Follow the 5:2 Diet: The Key to Effective Weight Management
Health
Step-by-Step Guide to Safely Relieving Bloating in Children
Space
The Journey to Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Martian Oceans
Animals
The Care of Offspring: The Reproductive Secrets of Guppies
Science
Science Could Regrow Your Lost Arm… on a Monkey’s Body
Animals
Stickleback Fish’s Secret to Adapting from Saltwater to Freshwater: How Genetic Mutations Enable Remarkable Adaptation
Fitness
HIIT: The Ultimate Shortcut to Efficient and Comprehensive Fitness