In the journey of exploring the universe, identifying planets capable of sustaining life has always been a top priority. However, recent studies have revealed the phenomenon of “tidal heating”—the rise in a planet’s internal temperature caused by gravitational forces between the planet and its host star—which can significantly alter the habitable zones within our galaxy. “Tidal heating not only pushes planets out of the ideal conditions for life but also completely changes their geological and climatic structures,” according to Rory Barnes, an astrobiologist at the University of Washington.
“The number of potentially habitable planets could decrease by as much as 50% due to the effects of tidal heating,” Barnes presented at the American Astronomical Society conference in 2023. This is especially critical when considering planets orbiting red dwarf stars, which constitute the majority in the Milky Way.
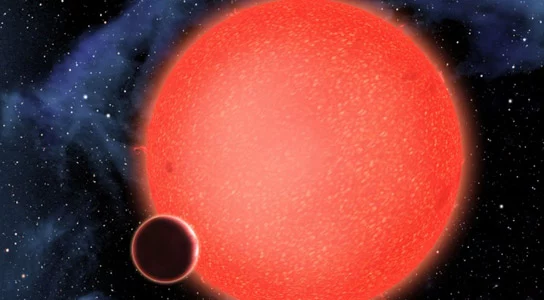
The habitable zone—often referred to as the “Goldilocks Zone”—is typically defined as the distance from a star where liquid water can exist on a planet’s surface. For red dwarf stars, this zone is located very close to the host star, where tidal forces are significantly stronger. The gravitational pull stretches the planet’s crust as it orbits in an elliptical path, causing internal friction and raising the planet’s internal temperature. This process can lead to intense volcanic activity, the release of toxic gases, or even the complete evaporation of surface water.
“Essentially, tidal heating acts as a planet’s self-destructive mechanism,” Barnes emphasized.
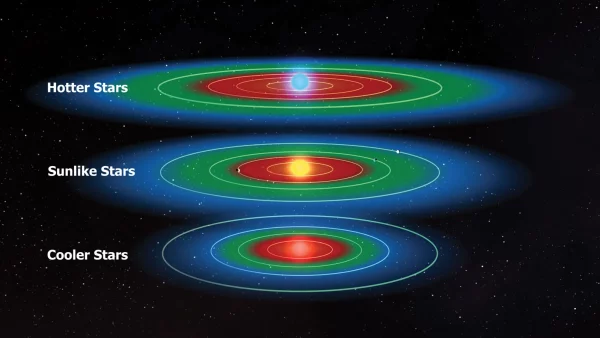
However, this phenomenon is not always a negative factor. Some planets may achieve a state of balance where volcanic activity helps sustain temperatures and creates an atmosphere suitable for life. This is particularly important for red dwarf stars, where the light is much weaker compared to the Sun. For instance, greenhouse gases released from volcanic eruptions could trap heat and prevent the planet’s surface from freezing.
Such studies not only provide new perspectives on the potential for extraterrestrial life but also underscore the fact that our understanding of the physical laws of the universe remains limited. Perseverance in research will continue to bring humanity closer to answering the question: “Are we truly alone in the universe?”


HPX24h > Space > Tidal Heating: A New Challenge for Extraterrestrial Life
Top Reads from This Category
Space
3D Lunar Map: A New Gateway to Understanding the Universe
Space
Could Our Universe Have Collided With Another Universe Billions of Years Ago?
Space
Over 100 Billion Planets in the Milky Way: Astonishing Discoveries About the Universe
Space
The Relationship Between Star Formation and the Activity of Supermassive Black Holes
Space
Scientists Believe Water Ice Could Exist on the Giant Asteroid Vesta
Space
Scientists Discover Dark Galaxy Located 10 Billion Light-Years from Earth
Space
The Two Largest Black Holes Ever Discovered
Discover New Topics
Space
Tidal Heating: A New Challenge for Extraterrestrial Life
Science
AI Can Simulate Evolution and Create Proteins – A New Opportunity for Breakthrough Medical Therapies
Fitness
Walking or Running: Which Is Better for Health and Weight Loss?
Animals
Bee Wax Bust of Nefertiti: The Perfect Fusion of Art and Nature
Healthy Eating
Foods That Support Depression Reduction: The Latest Scientific Nutritional Choices
Animals
Can Hyena Dogs Be as Smart as Primates?
Parenting Tips
How to Talk to Your Child About Drugs Effectively
Science
Discovering Enzymes That Stimulate Hair Regrowth: A New Opportunity in Hair Loss Treatment
Science
Stem Cells and Gut Cultures: Unlocking New Possibilities for Treating Digestive Disorders
Science
NSF Workforce Cuts – Which Path Will the U.S. Take to Stay Competitive in the Global Tech Race?
Fitness
Exercise – The ‘Miracle Cure’ to Awaken Overall Health
Animals
Stickleback Fish’s Secret to Adapting from Saltwater to Freshwater: How Genetic Mutations Enable Remarkable Adaptation
Fitness
Swimming: The Golden Key to Physical and Mental Well-Being